Currently Empty: 0.00 €
SONiC hands-on training - Module 5 - Lab 1 – OSPF Configuration
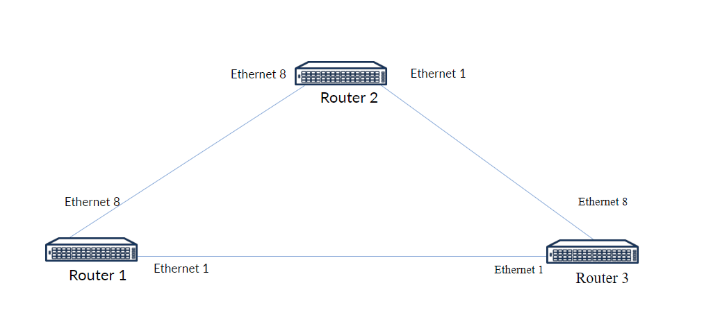
You are a network engineer tasked with configuring a simple OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) routing protocol in a triangular topology involving three routers:
- Router 1
- Router 2
- Router 3
The routers are connected via Ethernet interfaces, as shown in the diagram.
Instruction
Step 1: Assign IP Addresses on all of the Routers.
Log in to the switches (Router 1, Router 2, Router 3) using the default credentials, use the Klish CLI. Assign a proper IP Addressess to each of the port that is connected to other Router. Create an Loopback interface and assign a IP address to that interface.
Router 1:
- Ethernet 1 – 1.1.1.1/31
- Ethernet 8 – 1.1.1.2/31
- Loopback0 – 192.168.0.1/32
Router 2:
- Ethernet1 – 1.1.1.4/31
- Ethernet8 – 1.1.1.3/31
- Loopback0 – 192.168.0.2/32
Router 3
- Ethernet1 – 1.1.1.0/31
- Ethernet8 – 1.1.1.5/31
- Loopback0 – 192.168.0.3/32
Step 2: Create OSPF and Configure a router id for the OSPF process.
After you configured all of the interfaces on the router, you need to create an OSPF on a every router and configure a proper router-id on every OSPF session.
Step 3: Verify OSPF Configuration
To see if your configuration is properly applied, you need to first check in SONiC if the sessions
between the routers stays up. To do that, type in console “show ip ospf” and “show ip ospf neighbor”
Step 4: Check the connectivity between the routers.
From each router, ping the interfaces of the other two routers to confirm end-to-end connectivity.
- Default credentials: admin / YourPaSsWoRd
- Remember to add passive-interface command to your OSPF configuration to Loopback interface
- Be cautious about the OSPF area that you are using – It must match in this scenario between the switches.
- The names of the virtual computers are different in remote access to those shown on the topology. Virtual computers and their counterparts in remote access are motioned below:
- Router1 – mod5lab1-sw1
- Router2 – mod5lab1-sw2
- Router3 – mod5lab1-sw3
The purpose of the laboratory is to practice creating MCLAGs and PortChannels and how to use them in real environment.
Step 1: Assign IP Addresses on all of the Routers.
Router 1
interface Loopback 0
ip address 192.168.0.1/32
interface Ethernet1
ip address 1.1.1.1/31
no shutdown
interface Ethernet8
ip address 1.1.1.2/31
Router 2
interface Loopback 0
ip address 192.168.0.2/32
interface Ethernet1
ip address 1.1.1.4/31
no shutdown
interface Ethernet8
ip address 1.1.1.3/31
no shutdown
Router 3
interface Loopback 0
ip address 192.168.0.3/32
interface Ethernet1
ip address 1.1.1.0/31
no shutdown
interface Ethernet8
ip address 1.1.1.5/31
no shutdown
Step 2: Configure OSPF on Router 1, Router 2 and Router 3.
Router 1
router ospf
ospf router-id 192.168.0.1
area 0.0.0.1
network 1.1.1.0/24 area 0.0.0.1
network 192.168.0.1/32 area 0.0.0.1
passive-interface Loopback 0
Router 2
router ospf
ospf router-id 192.168.0.2
area 0.0.0.1
network 1.1.1.0/24 area 0.0.0.1
network 192.168.0.2/32 area 0.0.0.1
passive-interface Loopback 0
Router 3
router ospf
ospf router-id 192.168.0.3
area 0.0.0.1
network 1.1.1.0/24 area 0.0.0.1
network 192.168.0.3/32 area 0.0.0.1
passive-interface Loopback 0
Step 3: Verify OSPF Configuration
show ip ospf example:
sonic# show ip ospf
OSPF Routing Process, Router ID: 192.168.0.1
Supports only single TOS (TOS0) routes
This implementation conforms to RFC2328
RFC1583Compatibility flag is enabled
OpaqueCapability flag is disabled
Initial SPF scheduling delay 0 millisec(s)
Minimum hold time between consecutive SPFs 50 millisec(s)
Maximum hold time between consecutive SPFs 5000 millisec(s)
Hold time multiplier is currently 1 time is 92031756
SPF algorithm last executed 1065d4h22m ago
Last SPF duration 0.0s
SPF timer is inactive
LSA minimum interval 5000 msecs
LSA minimum arrival 1000 msecs
Write Multiplier set to 20
Refresh timer 10 secs
Number of external LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x0
Number of opaque AS LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x0
Number of areas attached to this router: 2
Area ID: 0.0.0.1
Number of interfaces in this area: Total: 2 , Active: 2
Number of fully adjacent neighbors in this area: 0
Area has no authentication
SPF algorithm executed 1 times
Number of LSA 2
Number of router LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x0
Number of network LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x0
Number of summary LSA 2. Checksum Sum 0x40f1f61000000000
Number of ASBR summary LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x0
Number of NSSA LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x0
Number of opaque link LSA . Checksum Sum 0x
Number of opaque area LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x0
Step 4: Check the connectivity between the routers.
Router 1:
# Ping Router 2’s Loopback
ping 192.168.0.2
# Ping Router 3’s Loopback
ping 192.168.0.3
# Ping Router 2’s Ethernet Interface (1.1.1.4)
ping 1.1.1.4
# Ping Router 3’s Ethernet Interface (1.1.1.0)
ping 1.1.1.0
Expected Output:
All pings should show success with low latency
Router 2:
# Ping Router 1’s Loopback
ping 192.168.0.1
# Ping Router 3’s Loopback
ping 192.168.0.3
# Ping Router 1’s Ethernet Interface (1.1.1.1)
ping 1.1.1.1
# Ping Router 3’s Ethernet Interface (1.1.1.5)
ping 1.1.1.5
Expected Output:
All pings should show success with low latency
Router 3:
# Ping Router 1’s Loopback
ping 192.168.0.1
# Ping Router 2’s Loopback
ping 192.168.0.2
# Ping Router 1’s Ethernet Interface (1.1.1.2)
ping 1.1.1.2
# Ping Router 2’s Ethernet Interface (1.1.1.3)
ping 1.1.1.3
Expected Output:
All pings should show success with low latency


